This article was originally published by the Pacific Forum on 14 January 2019.
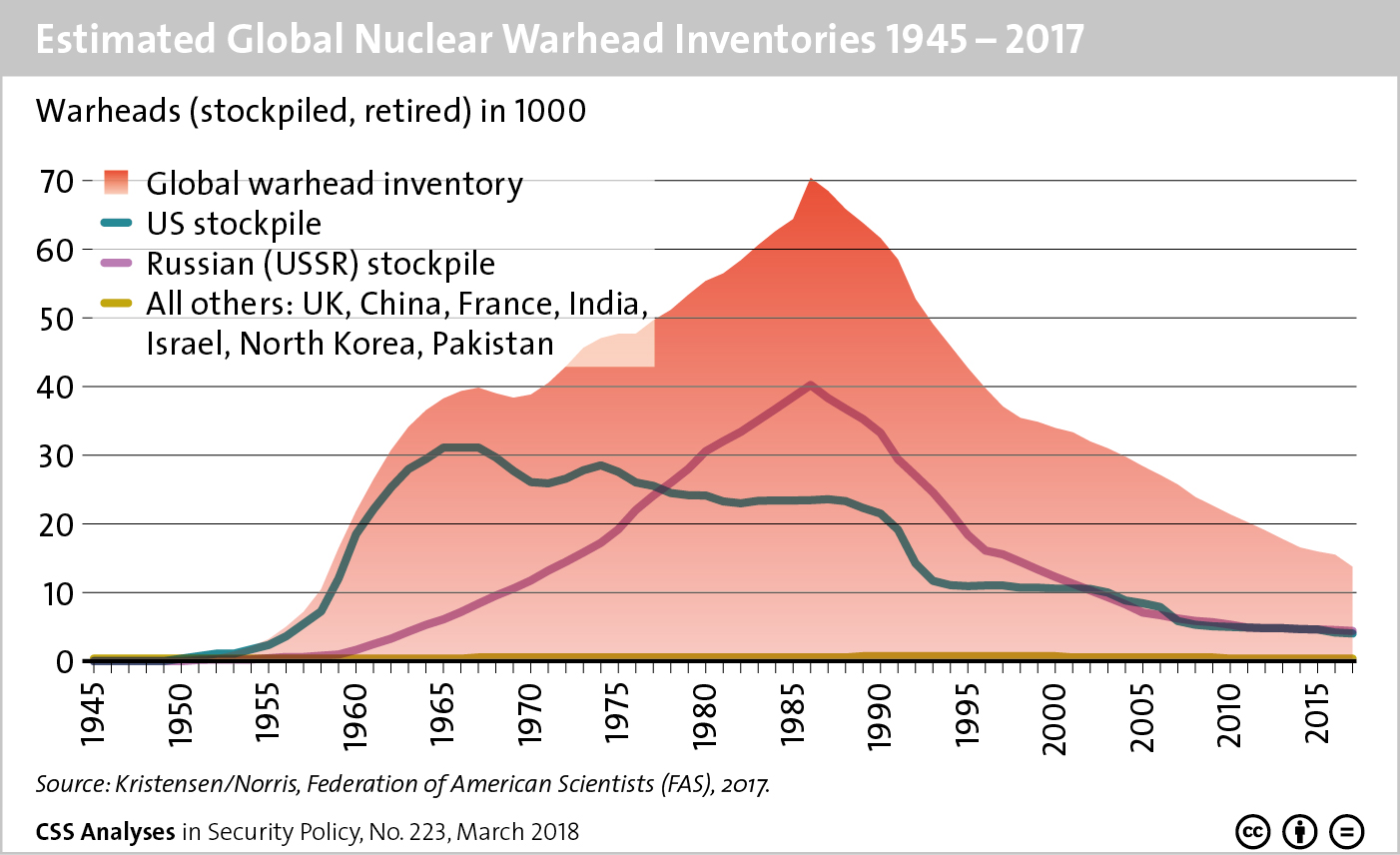
North Korea’s state-owned news agency ran a wire story with tremendous significance just before Christmas, making clear that unilateral denuclearization is not going to happen. As part of a detailed explanation of Pyongyang’s position, it said: “When we refer to the denuclearization of the Korean peninsula, it, therefore, means removing all elements of nuclear threats from the areas of both the north and the south of Korea and also from surrounding areas from where the Korean peninsula is targeted. This should be clearly understood.” The text also states that “the denuclearization of the Korean peninsula means ‘completely removing the nuclear threats of the U.S. to the DPRK.’”