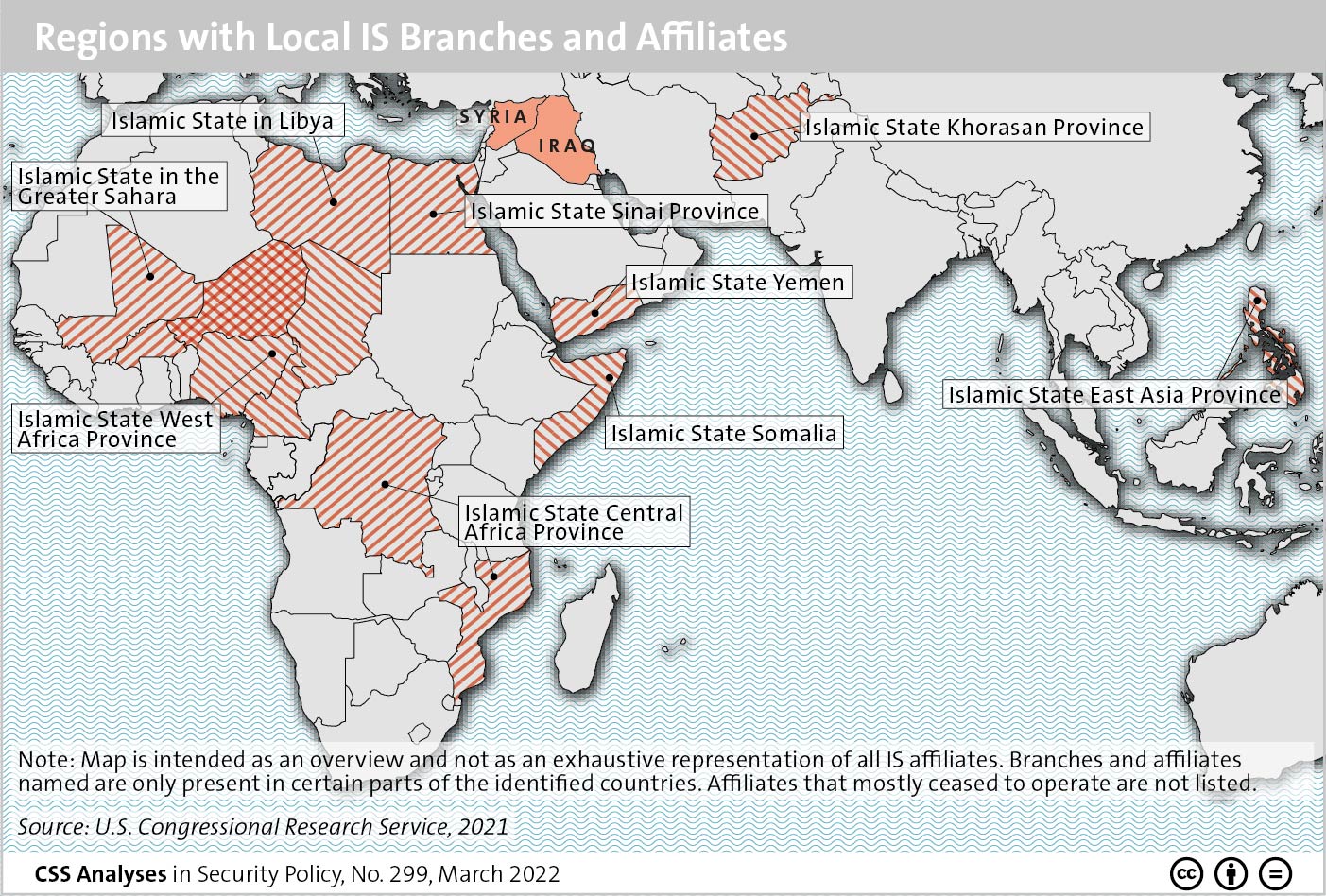
This week’s featured graphic shows the core IS’ state as of March 2022 as well as its affiliates in Africa, the Middle East and Asia. For a deeper assessment of the danger the IS still poses, read Fabien Merz’ CSS Analysis in Security Policy here.

This week’s featured graphic shows the core IS’ state as of March 2022 as well as its affiliates in Africa, the Middle East and Asia. For a deeper assessment of the danger the IS still poses, read Fabien Merz’ CSS Analysis in Security Policy here.

This article was originally published by the Small Wars Journal on 6 March 2019.
Introduction
The Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham (ISIS) routinely kidnaps, recruits, and employs child soldiers to carry out its operations. In recent years, ISIS possessed major land holdings in Syria and Iraq, and has carried influence on a global scale; however, the overwhelming international military response to ISIS’ brutality has largely driven this terrorist organization out of its formerly held territories. As ISIS members are displaced through battlefield losses, reintegration of former ISIS members remains a key challenge globally. ISIS has frequently used children as a part of its military operations, and hundreds of these children have been indoctrinated into ISIS ideology. The international community now faces a critical issue with the rehabilitation of ISIS children. This population was raised in a hyper-violent environment and has largely never been exposed or integrated into conventional society. As these children and their families flee to non-ISIS controlled areas or home countries, they pose a lifelong terrorism threat to the international community.

This article was originally published by War on the Rocks on 12 March 2018.
Nearly three years on from the Islamic State’s high water mark in the summer of 2015, there are several lessons that the United States and its allies can discern from the terrorist group’s meteoric rise to control large parts of Iraq and Syria to the loss of its physical caliphate late last year. The steady decline in ISIL’s fortunes is striking given the palpable fear its rise in the summer of 2014 sparked across Washington, when a common question circulating within the policy community was whether Baghdad itself might fall. Many of these takeaways will be relevant to U.S. policymakers as they attempt to prevent the group from reconstituting itself in the coming months.

This article was originally published by the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies (RSIS) on 22 August 2017.
Synopsis
As the Western Mindanao Command (Westmincom) closes in on the dwindling number of IS militants in Marawi, various terrorist tactics learned from the wars in Iraq and Syria are being replicated to worsen the conflict in southern Philippines and spread IS influence in the region.
Commentary
The Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP) has managed to recapture most of Marawi back from the Maute Group and its acolytes despite the military’s lack of familiarity with urban warfare and the terrain. Westmincom has made “great advances” addressing the “complicated” issues on the ground even though it missed the deadline for retaking Marawi fully or wiping out terrorism from Mindanao by June 2017.
However, for the Maute Group and other terrorist groups in Mindanao, the eventual loss of Marawi will not be so much of a setback as the beginning of bolder military moves to capture territory, even if briefly, to demonstrate their fighting capability and rally support for the so-called Islamic State (IS) in the region, especially in the wake of IS military defeats in Iraq and Syria.

This article was originally published by the Small Wars Journal on 9 July 2017.
Online, the Islamic State is a technologically savvy, sophisticated, and nimble organization that learns from its mistakes and from the actions of the Western intelligence services and NGOs that have sought to counter it. It is no secret that past and current efforts to reach potential terrorists before they can become radicalized and committed to a path of jihad and terrorism have proved inadequate. To use the language of online marketers, countering ISIS’s online activities will require quality content disseminated on a massive scale, with careful product placement. Placing counter-messaging products into platforms and forums that extremists frequent will increase the chances of potential terrorist recruits coming into contact with narratives outside of ISIS’ control.
ISIS’s cyber efforts have paid off; the FBI told Congress in July 2016 that “the message of radicalization spreads faster than we imagined just a few years ago.”[i] The number of foreigners who have been inspired by the Islamic State’s online propaganda to travel to Syria and Iraq (or elsewhere) and participate in the fighting is unclear, but most estimates place the tally at more than 20,000. Others have been set on the path of radicalization by ISIS’s online propaganda and have become “lone wolf” attackers in the United States or in Europe.[ii] Demographically speaking, the people who ISIS is most interested in targeting for recruitment came of age in the twenty-first century as “digital natives”; they have lived their entire lives surrounded by ubiquitous online communications and have embraced it in technologically sophisticated ways.[iii] ISIS knows how to appeal to these potential jihadis. Reaching them with counter-messages will require a sophisticated and multi-faceted approach.