Image courtesy of Flickr. President Santos signing the peace agreement with the FARC on 26 September 2016. Less than a week later, the deal was rejected in a plebiscite.
Mediation Perspectives is a regular series of blog contributions by the CSS Mediation Support Team and occasional guest authors.
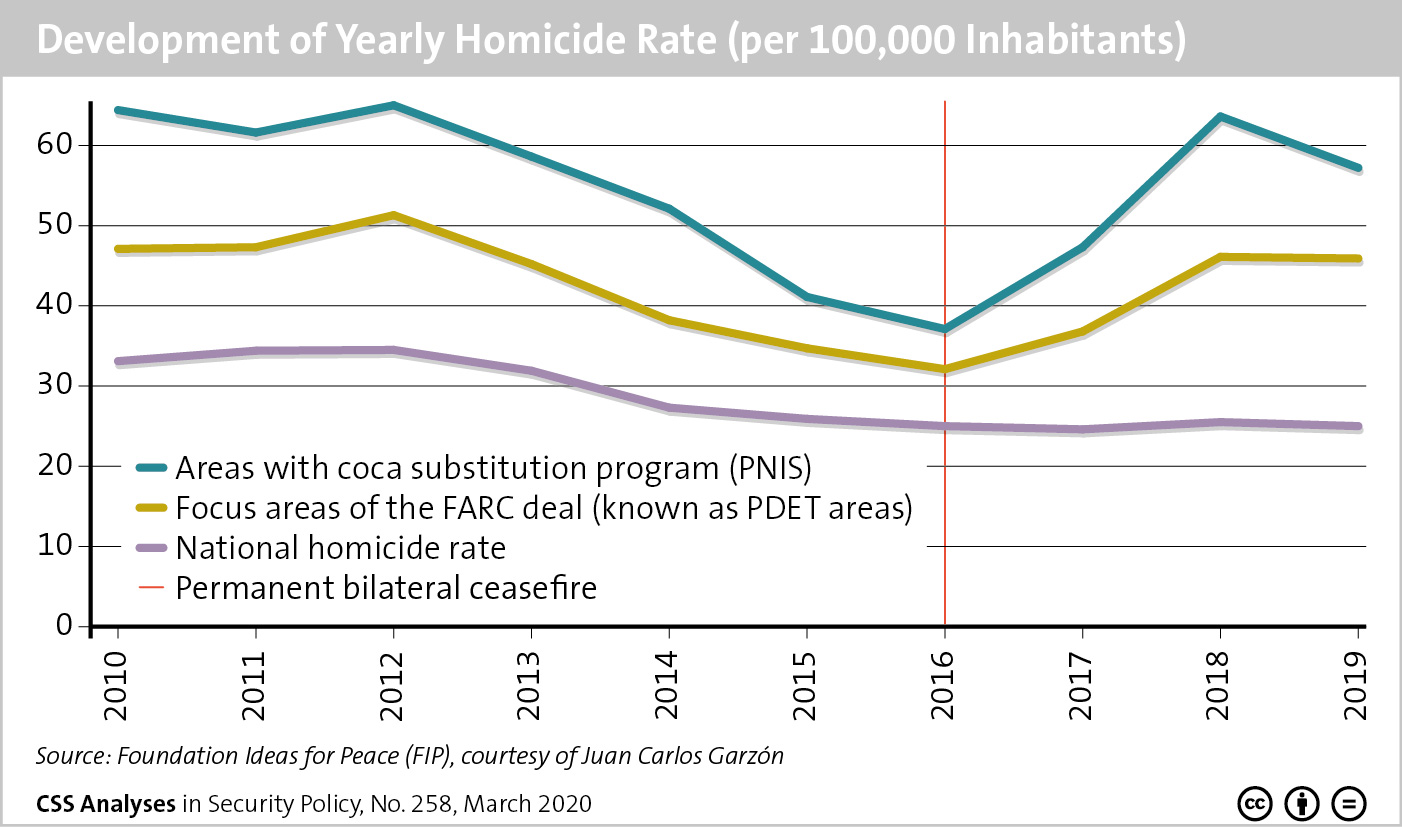
Intrastate conflicts are notoriously difficult to settle. In many regions of the world, from Afghanistan and Myanmar to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, citizens have grown up during war, only to see their children or even grandchildren born into continued conflict. That is not to say that long-standing enemies never manage to reach a negotiated settlement. In Colombia, after more than half a century of fighting, the government reached a peace agreement with the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias de Colombia, FARC) in 2016. But implementation is slow, and the state remains at war with the country’s last guerrilla organization, the National Liberation Army (Ejército de Liberación Nacional, ELN).