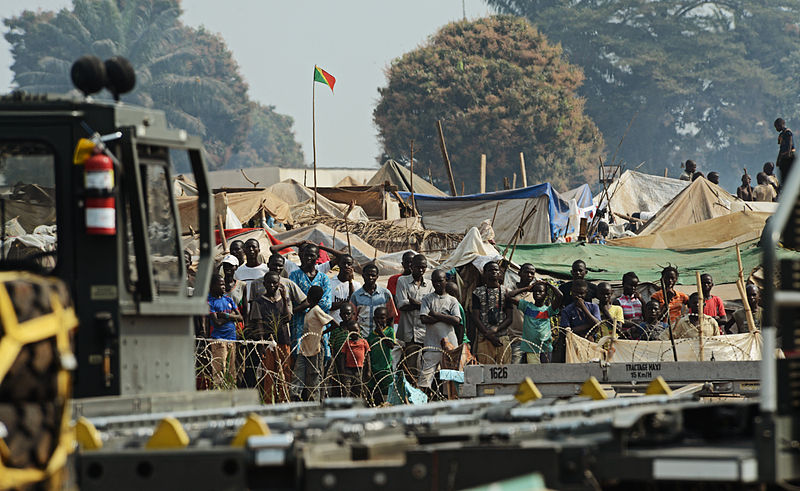
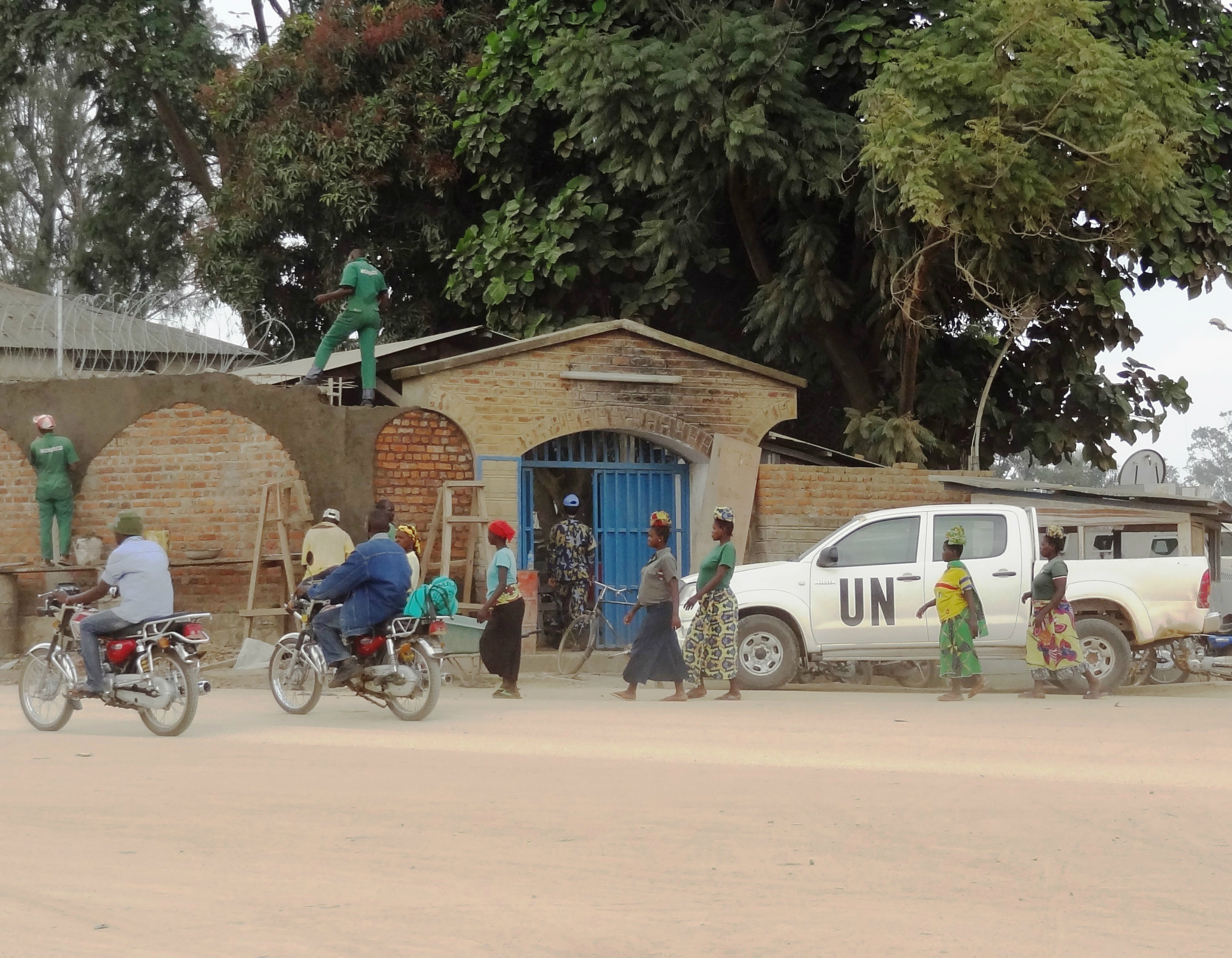
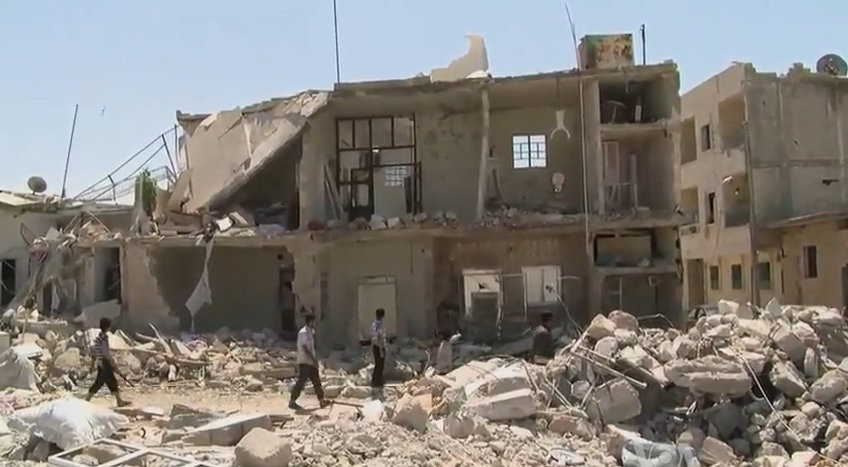
The crisis in the Central African Republic (CAR) has left humanitarian organisations, international peacekeepers and observers frantically searching for solutions to stop the conflict. Now, to make matters worse,the Afghan Taliban and the notorious al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM) – which, together with its allies, occupied northern Mali in 2012 – have denounced what it describes as the ‘ethnic cleansing’ of Muslims in the CAR. AQIM also issued a warning against France for its alleged complicity in the violence, saying the ‘supposed peacekeepers’ have launched a ‘crusade against Islam’ and that France will be punished for doing so. Given that ordinary Muslims in the CAR are clearly being targeted and tens of thousands of Muslims are fleeing the country, should this threat be taken seriously?
David Zounmenou, Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Security Studies (ISS) believes that AQIM is still smarting after its defeat against France in Mali last year and that their warnings are not to be taken lightly. The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) also met last week to discuss the situation in the CAR and has pleaded for dialogue and national reconciliation – another sign that the crisis has now taken a decidedly religious turn. Yet, Zounmenou strongly warns against casting the conflict in the CAR in the same mould as other crises in Africa that are rooted in conflict between locals and radical Islamist groups, such as in Mali or Somalia.