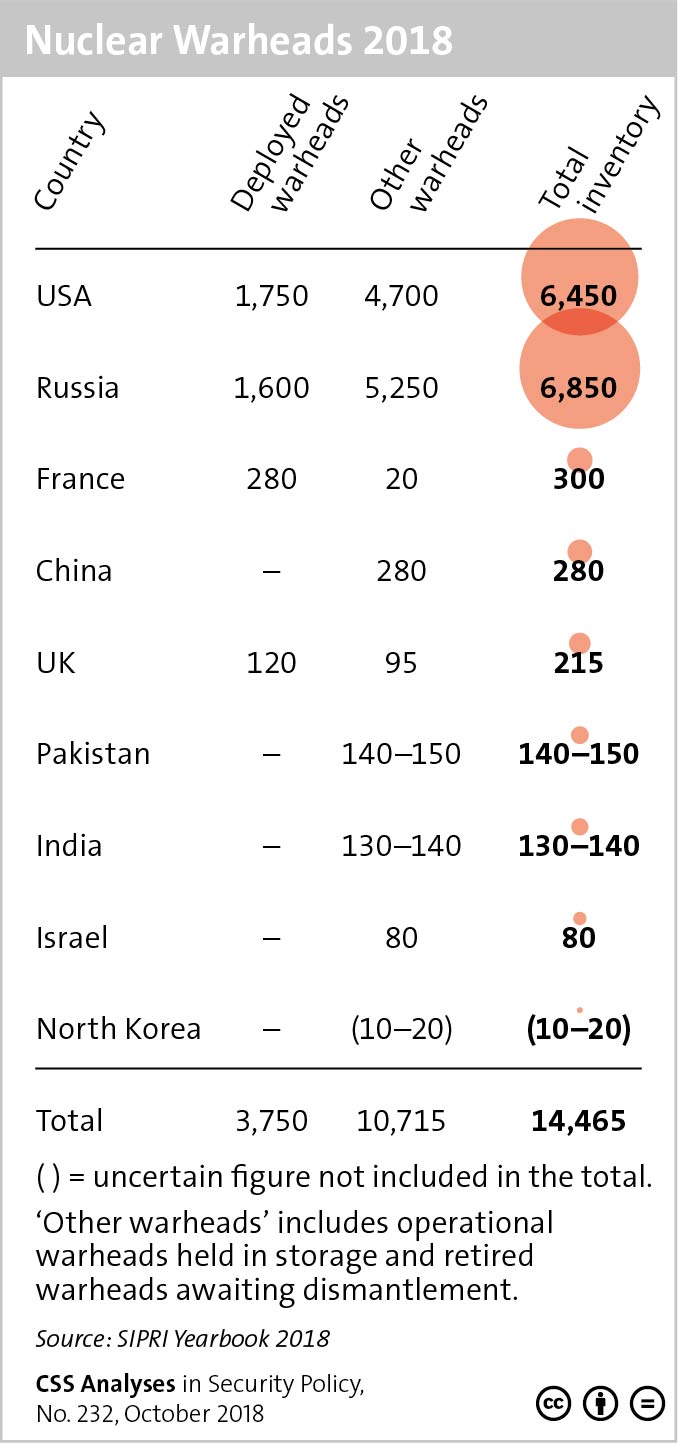
This graphic shows the number of nuclear warheads owned by each country known to have nuclear weapons. For more on trends in nuclear arms control, see Oliver Thränert’s CSS Analyses in Security Policy series here.

This graphic shows the number of nuclear warheads owned by each country known to have nuclear weapons. For more on trends in nuclear arms control, see Oliver Thränert’s CSS Analyses in Security Policy series here.

This article was originally published by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) on 29 July 2019.
The states parties to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC) gathered in Geneva from 29 July to 8 August for a series of Meetings of Experts. Among other topics, states reviewed scientific and technological developments that impact the objectives of the treaty. Additive manufacturing (AM)—also referred to as 3D printing—is one of the technologies that is starting to receive attention, next to more well-known biotechnologies and genetic engineering techniques. Advances in AM have been met with concerns over its potential to facilitate the development, production, delivery and thus proliferation of biological weapons—and have highlighted the potential role of export controls in reducing these risks.
This graphic shows the number of nuclear warheads owned by each country known to have nuclear weapons. For more on trends in nuclear arms control, see Oliver Thränert’s recent addition to the CSS Analyses in Security Policy series here. For more CSS charts, maps and graphics on proliferation, click here.

This week the ISN looks at the causes and consequences of a global nuclear renaissance. We ask whether nuclear power is a false prophet for a planet imperiled by climate change and assess the difficulty of reigning in those that seek to turn energy into weapons.
The Special Report includes the following content: